Gauss's Law
Gauss's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Area Vector, Gauss Theorem in Electrostatics, Electric Field due to a Charged Sphere Using Gauss's Law, Condition for the Validity of Gauss Theorem, and Gaussian Surfaces for Various Charge Distribution.
Important Questions on Gauss's Law
Which law is used to derive the expression for the electric field between two uniformly charged large parallel sheets with surface charge densities and respectively:
A charge is placed at the mouth of a conical flask. The flux of the electric field through the flask is
flux lines are going inside an area of a certain volume and flux lines are passing through that area are going out. How much charge is there within that field?
The electric field acts in the space in which a cylinder of radius and length is placed with its curved surfaces parallel to axis. The charge inside the volume of cylinder is
Assertion: Gauss's law can't be used to calculate electric field near an electric dipole.
Reason: Electric dipole don't have symmetrical charge distribution.
A hollow cylinder has a charge coulomb within it. If is the electric flux in units of associated with the curved surface , the flux linked with the plane surface in units of will be
The potential (in volts) of a charge distribution is given by
for
for .
does not depend on and . If this potential is generated by a constant charge per unit volume (in units of ) which is spread over a certain region, then choose the correct statement.
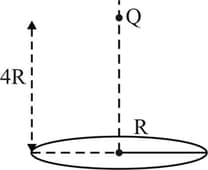
A charge is placed at a distance above the centre of a square surface of side length . The electric flux through the square surface due to the charge would be?
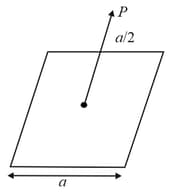
Figure shows a closed surface which intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at the point the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
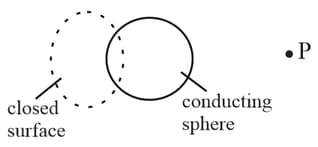
The figure shows a thick metallic sphere. If it is given a charge then an electric field will be present in the region
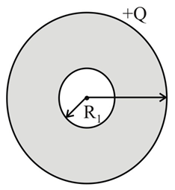
Which of the following represents the correct graph for electric field intensity and the distance from the centre of a hollow charged metal sphere or solid metallic conductor of radius
Gauss law is given by if net charge enclosed by Gaussian surface is zero then-.
A charge is placed at a distance of above the centre of a disc of radius The magnitude of flux through the disc is Now a hemispherical shell of radius is placed over the disc such that it forms a closed surface. The flux through the curved surface (taking the direction of area vector along outward normal as positive), is -
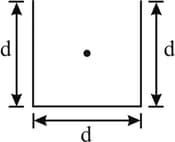
A cubical box contains charge at its centre. The total electric flux emerging from the box is:
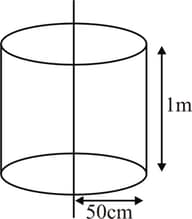
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius The charge per length of the wire is coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius and length symmetrically encloses the wire as shown in fig. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is -
As shown in the figure, a charge is placed at the centre of the cubical vessel (with one face open) is placed at the centre of the cubical vessel (with one face open) as shown in the figure. The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is
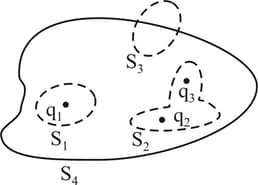
Three charges have been placed, as shown in the figure, in four surfaces and electrical flux emitted from the surface in will be -
Total flux coming out of some closed surface is:
In a uniformly charged sphere of total charge and radius the electric field is plotted as a function of distance from the centre. The graph which would correspond to the above will be:
Consider a thin spherical shell of radius with its centre at the origin, carrying uniform positive surface charge density. The variation of the magnitude of the electric field and the electric potential with the distance r from the centre, is best represented by which graph?
